As the world shifts towards a cleaner, electrified future, one metal stands at the forefront of...
Driving Decarbonization: The Rising Demand and Vital Role of Copper
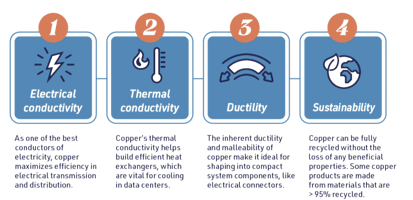
Copper is a remarkably versatile and indispensable material in our modern world. With unique electrical, thermal, and physical properties, copper is critical in industries and applications that are essential to our contemporary way of life. As the world increasingly relies on advanced technologies, renewable energy, and modernized infrastructure, the rising demand for copper highlights its pivotal position in powering the innovations and green initiatives for today and beyond.
Electric Vehicles
The growing popularity of electric vehicles is a primary driving force behind the rising demand for copper. Copper is a key material used in EVs, charging stations, and electrical infrastructure that supports EV charging.
 Light-duty electric vehicles use about 2-½ times the amount of copper compared to a conventional gas-powered vehicle. Medium and heavy-duty vehicles use even more because their battery packs are notably larger. In 2023, over 1.1 million battery-electric vehicles were sold in the U.S., a 48% increase over 2022.
Light-duty electric vehicles use about 2-½ times the amount of copper compared to a conventional gas-powered vehicle. Medium and heavy-duty vehicles use even more because their battery packs are notably larger. In 2023, over 1.1 million battery-electric vehicles were sold in the U.S., a 48% increase over 2022.
In 2023, 19 EV models sold in the U.S. had a range of 300+ miles, compared to only 5 in 2021. Additionally, as of May 31, 2024, the lowest-cost EV model in the U.S. with a range of 300+ miles is $35,000, which is $12,000 less than the $47,000 average cost of all U.S. cars.
Electrical Infrastructure and Green Technologies
The use of copper in electrical infrastructure dates to the early 1800’s. Being the most conductive non-precious metal, copper has been an essential material for power transmission and distribution systems throughout the history of modern electrification.
Today, the rapid expansion of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources is another major driving force for the copper industry. The material is critical in electrical components such as generators, transformers, and wiring in solar, wind, hydrogen, and hydropower sources.
Copper plays a key role in the design and functionality of switchgear and panel boards used in new energy systems to manage electrical flows. Copper busbars, terminals, and connectors within switchgear and panel boards ensure safe and efficient power distribution, minimizing energy losses with minimal space and enabling reliable operations of renewable energy sources and other new energy technologies. Copper is also a key component in energy storage technologies like battery systems, which are now often coupled with solar.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Centers
Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence have led to an unprecedented demand for high-performance computing power, driving the growth of energy-intensive data centers. These data centers, which house powerful servers and infrastructure, rely extensively on copper to provide power and cooling to their critical components using power cables and wiring, busbars and strips, and electrical connectors. 
Copper’s excellent electrical and thermal conductivity and physical durability make it well-suited for navigating the tight space constraints within densely packed data centers, where efficient power delivery and heat management are critical. As AI algorithms become more complex and data volumes increase, more efficient power distribution, and adequate thermal management are imperative. Copper’s eminent conductivity, durability, compactness, and life-cycle cost-effectiveness make it a critical material in the design and construction of modern data centers.
Industrialization and Urbanization
Industrialization and urbanization are additional significant factors driving the demand for copper worldwide. Copper is used in construction, plumbing, electrical wiring and communications, housing, and transportation.
In 2023, 45% of copper and copper alloys in the United States were used in the building sector. As the United States grows toward a more sustainable and energy-efficient society, more buildings are incorporating copper piping, wiring, and HVAC components, such as heat pumps, which replace gas-burning furnaces. Copper also makes remarkable roofing and wall cladding, capable of not only effectively sustaining their integrity for well over a hundred years, but offering artistic beauty as it blends architecturally.
Consumer Electronics
In the Digital Age, copper has become an increasingly vital material for a wide range of consumer electronics. As technology progresses quickly, the demand for copper in devices like smartphones, computers, TVs, audio equipment, gaming consoles, small appliances, and other connected gadgets has grown significantly.
Copper has proven to be the most recyclable and highest-performing material for these devices. Its exceptional ability to be recycled repeatedly without diminishing its quality and performance makes it a preferred material for use in the production of consumer electronics, supporting the sustainability of these devices through multiple life cycles.
The miniaturization of electronics also contributes to the rising demand for copper. As product sizes become smaller, using copper in compact designs enables maximum functionality. Copper's strong electrical conductivity and thermal management capabilities make it an essential material for enabling the compact, high-performance designs of modern consumer electronics and mobile devices.
Future Outlook
The global demand for copper is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. This rise is driven by the United States’ transition to more sustainable infrastructure, manufacturing, and construction, which rely heavily on copper’s use in EVs, renewable energies, and energy-efficient buildings.
Copper’s exceptional properties make it an indispensable material powering the modern world across an array of industries. The outlook for long-term copper demand will remain robust, providing an unprecedented opportunity for the copper industry to meet the increasing demands while advancing sustainability initiatives.
To learn more about why copper is key to a carbon-free future, watch our recent on-demand webinar with Design World here. We cover copper’s essential properties, the U.S.'s position in the global copper network, and the expanding markets driving demand.